Indices are a measurement of a share group’s price performance. Trading indices permit you to expose yourself to a whole economy or sector at once, with only a single position open.
With indices strategy, You may speculate on indices price appreciating/depreciating without being obligated to take ownership of the underlying asset. CFDs make this possible. With more trading hours than a lot of markers, indices are a highly liquid market to trade. There’s every likelihood of longer exposure to possible opportunities.
Indices strategy stands for substantial returns
Records of the previous two decades of trading on S&P500 prove that indices trading is highly rewarding. Per data, in a year, the return percentage is decidedly positive, translating to a 6.3% gains per year average. At 61.25% there’s the frequency of gains average. Per data, bearish moves are stronger than bullish moves. There have been a minimum of four sell-offs above 11% over the preceding two decades. On the other hand, there is merely one double-digit gaining month for the S&P500 over the same period.
Stock markets do have innate trends. Indices are a vastly preferable instrument over the long term. This is true when we search for an asset to buy and hold. Uptrends are comparatively dependable, steady, and long-lasting. On the other hand, bearish moves are generally shorter, albeit more dramatic. Sharper periods of weakness do attract many.
However, the continual wish to pick market tops will generally lead to anxiety. It is, therefore, more sensible to make use of indices’ bullish nature to trade with that trend instead of calling tops against the tops.
Indices strategy for bullish indices
Stocks appreciate more frequently than they depreciate, implying that a bullish long-term training strategy is reasonable. Reinvesting dividends adds a compounding effect where your account develops proportionally over time. When the stock undergoes ex-dividend, counteracting a share price drop, on a spread betting account you will get a dividend adjustment.
Nonetheless, overnight charges imply that generally long holds will be more efficient thru a leveraged futures contract, or non-leveraged stock portfolio or ETF, which does.
How do I trade indices? Or what is the best trade indices strategy? Or day trading indices strategy
You may trade indices thru a CFD, ETF, option, or index future. They all have merits and demerits.
Not a standardised exchange-listed instrument, a CFD is essentially a betting instrument offered for speculation in a given market. CFDs are important since they enable trading in micro-lot size. PrimeFin permits clients to trade CFD contract sizes from as low as GBP 1 per point on the FTSE 100 index. This permits the speculating without risking the sort of money index futures would need. As an indices strategy, CFDs disadvantage is that firms offering the CFDs have to make money off the price spread.
Index Futures are index exchange traded, having an expiry date and thus the pricing includes a forward interest premium as well as a discounted dividend. Index CFDs are easier to understand, trading as they do at the spot price, not expiring.
In this regard, ETFs do not have much over CFDs. 100 shares is a standard lot. Going beneath the standard lot size your trade would likely be routed to odd-lot dealers rather than directly handled thru regular channels. As an indices strategy, CFDs definitely make for more flexibility.
A CFD or Contract for Difference refers to a pact or contract of exchange between seller and buyer that sets forth a condition in which the buyer has to pay the difference amount between the asset’s current value and contract value to the seller. Read more about the CFD trading guide.
When to trade indices: best indices strategy
Professionals choose to trade during high volatility. This means the chosen market has just opened or it is about to close. Moreover, key economic data or global news events, like the US non-farm payrolls or interest rate announcements trigger above average volatility.
How important is timing?: best indices strategy
We like to think that we may profit from the news in case we act faster than others. That’s a fallacy.
- Anticipation moves the market. Buy the rumour, sell the fact. You would be broke if you every bit of press-published good news.
- The market reacts to the difference between the actual news and what had been the expectation. The unemployment rate could plummet 0.2 per cent, and the market declines since it expected a 0.4 percent drop.
- Action is not a signal for immediacy. When did the Fed lower interest rates? When did the market start responding? as far as interest rates go, it always takes more than one move by the Fed prior to there being a reaction.
Admittedly, economic data and news events catalyse price movements. we do not have to analyse them to trade successfully. All such info is finally mirrored in the price chart as price action. Analysing price action does, however, tell you who is the main influencer. Those losing control – be they buyers or sellers – are also revealed. Index reversals thus become predictable, enabling you to make money.
Reversal patterns: an important indices strategy
Reversal patterns offer you an advanced warning when an index is most likely to turn around and start a new trend, and how far an index is potentially going to move in the direction opposite. Reversal patterns, while being quite fallible, do put the odds of success in your favour.
There are two reversal patterns you have to be aware of:
- Double tops/bottoms;
- Head and shoulder tops/bottoms.
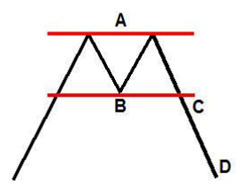
Double tops/bottoms
Double tops/bottoms form as an index price hits a support or resistance level two times prior to the index turning around, moving in the opposite direction. Bearish reversal patterns, double tops are the opposite number to double bottoms, which are bullish reversal patterns.
When an index is in an upward trend, it will give a double top. When an index is in a downward trend, it will give a double bottom. Instructive indices strategy, that!
- A or Resistance level
A horizontal or slightly angled level of resistance;
- B or Support level
A horizontal or slightly angled level of support ;
- C or Breakout point
The point at which the index breaks up above the horizontal level of resistance -a triple bottom – or the point where the index breaks down below the horizontal level of support – a triple top;
- D or Price projection
The price to which the index will potentially plummet following its breaking out of the triple top formation, or the price to which the index will potentially ascend following its breaking out of the triple bottom formation. The distance the index is projected to shift equals the distance between given airport and resistance levels.
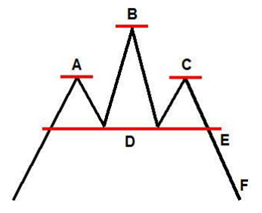
Head and shoulder tops/bottoms
Head and shoulders tops are reversal patterns form as the price nudhes a resistance level – the first shoulder – subsequently breaking thru the first resistance level – forming the head – subsequently hitting the first resistance level again – the second shoulder. This indices strategy rewards your attentiveness.
- A or left shoulder
A horizontal or slightly angled resistance level – head and shoulders top – or a horizontal/bit angled level of support -head and shoulders bottom;
- B or Head
A higher horizontal or bit angled level of resistance -head and shoulders top – or a lower horizontal or bit angled level of support -head and shoulders bottom;
- C or Right Shoulder
A horizontal or bit angled level of resistance in line with the left shoulder – head and shoulder top or a slightly horizontal or bit angled level of support in line with the left shoulder – head and shoulders bottom;
- D or Neckline
Aa horizontal, or bit angled level of support-head and shoulders top or a horizontal or bit angled level of resistance – head and shoulders bottom;
- E or breakout point
The point at which the index brakes up above the neckline -head and shoulders bottom or the point at which the index breaks down below the neckline – head and shoulders top ;
- F or Price projection
The price to which the price will potentially plummet following its breaking out of the head and shoulders bottom formation. Also, the price to which the index will potentially ascend following its breaking out of the head and shoulders bottom formation. The distance the index is projected to move equals the distance between the head and the neckline.
Correlation between indices: Make your indices strategy count
Indices are either region-based or sector-based, serving as indicators for ongoing market sentiment. Since, however, economies are deeply intertwined, it comes an as little surprise that indices are highly correlated.
The correlation between global economic events and prominent indices price patterns is an important point of departure for traders intending to participate in index markets. You may well, for instance, know where the DAX is trading these days, if it opened lower or with a bullish gap. However, you must know what this signifies for you as a trader, and how you may best capitalise on dormant opportunities.
Indices markets: breeding grounds for best indices strategy
The most vital info regarding an index frequently given besides the current price is the daily fluctuation – as a percentage – and the points by which it has ascended or descended since markets opened.
Take the DAX, for instance. Provided you deem Germany to have positive economic prospects you’d be buying DAX CFDs hoping that companies in that country would haul up the index’s price.
Indices may indeed appreciate not son much as an outcome of actual economic growth, but more due to an appreciation in risk tolerance. such deviations, however, do not last that long. Inevitably a price correction follows. Traders frequently compare indices performance from diverse regions to spot and make the most of opportunities.
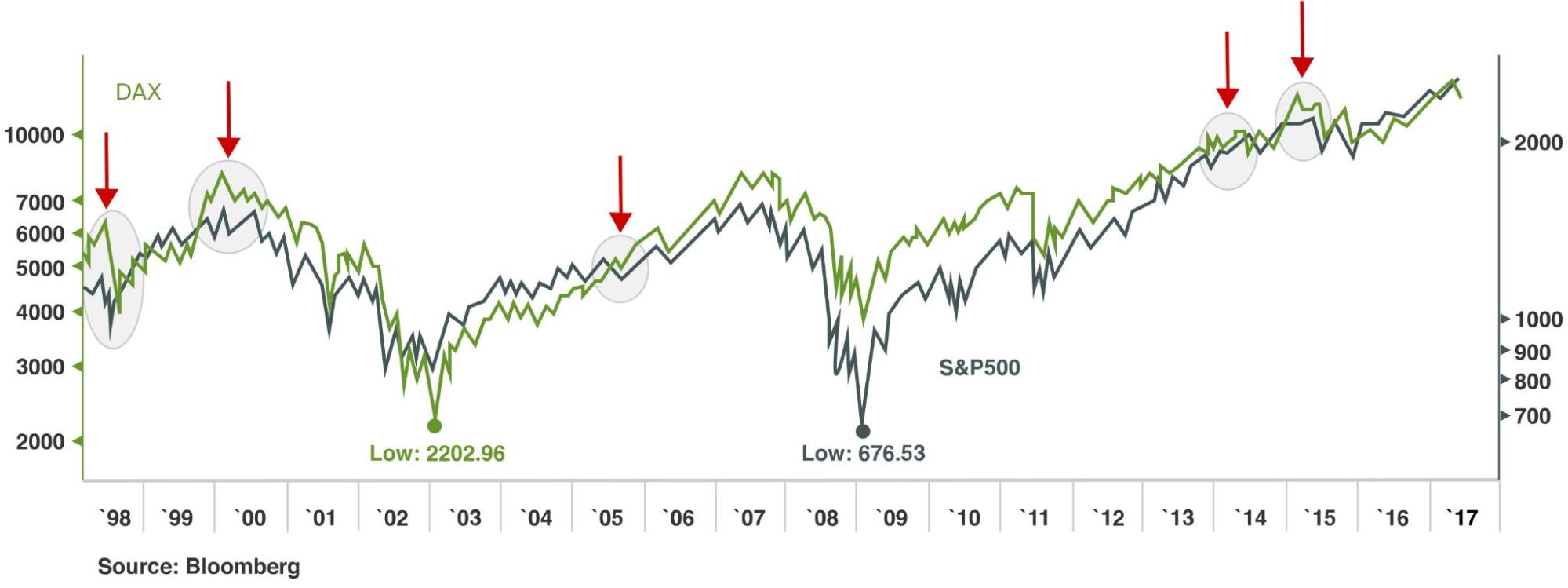
Correlation between DAX and S&P500: Your indices strategy is globally relevant
The S&P 500 index is widely deemed a reliable equity market barometer. Trades do follow it as an indicator of major industries’ respective strengths. The German stock market’s performance is similarly reflected on the DAX.
There’s a strong correlation between the two indices. When DAX and S&P500 do not move in sync, this is frequently interpreted as a price anomaly – thereby presenting a trading opportunity.
Indices strategy to take advantage of differences between indices
Assessing how the markets will move in the event of a price anomaly, you have to be aware of the differences between indices, apart from what makes each of them unique.
Constituent companies
The US economy is mainly consumer-driven. The S&P500 represents financials, IT, and healthcare taking up close to half of the index. Conversely, Germany is focused on exports. In that regard, it is chemicals that are Germany’s forte.
Total return versus price return index: impactful indices strategy
Total return indices versus price return indices
Total return indices measure constituent companies’ strength, the assumption being that all dividends are reinvested. DAX is a total return index and a primary reason why it pushes higher. Conversely, the S&P500 is a price return index, implying that return calculation takes no account of dividends.
When indices’ prices diverge, the above factors ought to be born in mind prior to determining the market side you will trade. Most prefer trading indices thru CFDs. The latter permits traders to profit from both shooting and plunging prices. Traders, therefore, open long positions, provided as per you the index will ascend. On the other hand, you can short positions or sell, in case it appears to you the index will plummet.
Nonetheless, for active leveraged traders, dividends are not one doctor to consign to neglect. This is what ads an underlying bullish trend to stock markets.
Be that as it may, in case a trader is to approach a trend following index strategy, it is indeed sensible to search for bullish setups including higher highs and higher lows. Employing that as a bullish confirmation signal, traders may use a lot of diverse strategies to enter the trend.
Consolidation /retracement breakout: a wise indices strategy
Uptrends frequently do not see huge retracements the bullish sentiment implying that you’d generally see smaller to mid-sized retracements. A trader may buy on the breakout into new highs, where a slight retracement or consolidation would be used to place a stop below. Deeper retracement entry strategy: recommended indices strategy
The use of deep Fibonacci retracements may offer traders the chance to enter trades for comparatively affordable relative to recent price, cutting down the stop loss’s size to raise their risk to reward profile. Markets do not move in a linear manner. There will be pullbacks to offer buying opportunities.
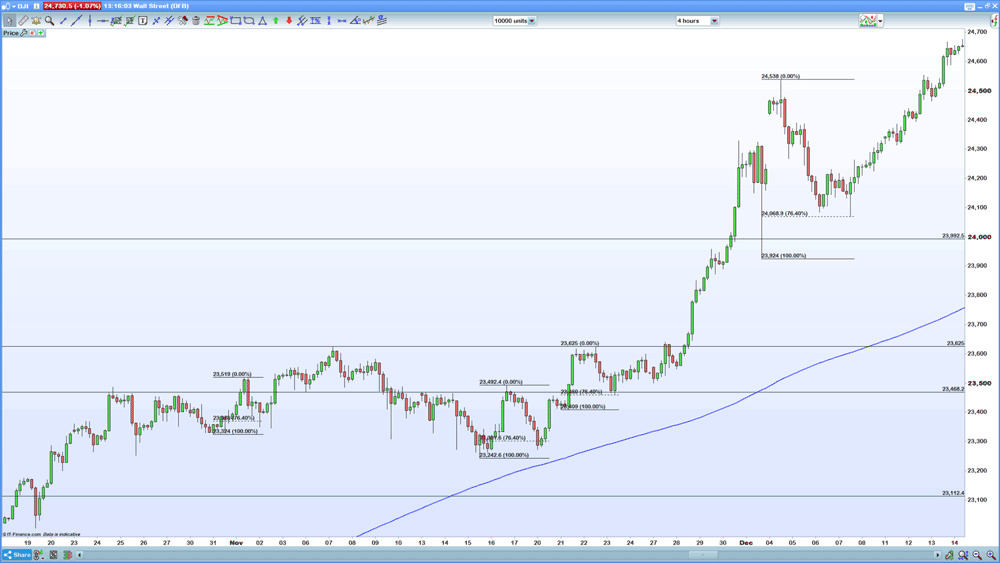
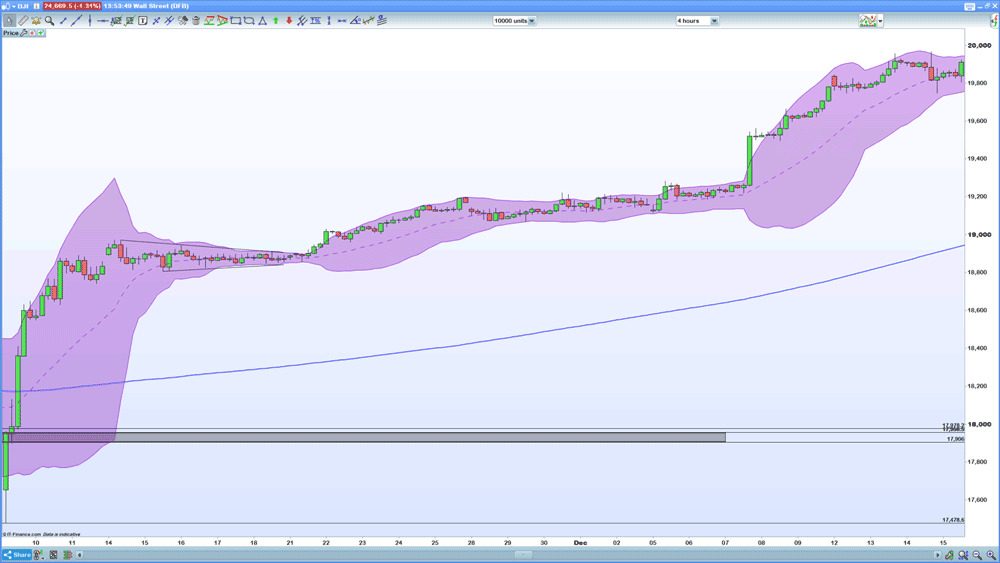
Notwithstanding our observing deep retracements – 61.8 – 76.4% – such moves frequently take place during consolidation or volatility.
The two 76.4% retracements on the chart’s size culminate in an uptrend consolidation period.
A trader may take the strategy above buying on the breakout on the contrary you ought to wait on the break thru the first swing high on the way down, anticipating the way for a failed attempt to break into a new low. Such a move frequently offers deep retracements, thanks to the battle between bulls and bears. That gives us two successful trades where you buy at the 76.4% Fibonacci retracement and place a stop below the preceding swing low.
The third example is from early December. The volatility does not break the overall trend of higher lows and highs, offering us rather a buying opportunity at the 76.4%retracement.
Bollinger entry: an indices strategy for profits
Bollinger bands give another possible tool useful to trailers, going back into the lower threshold of the indicator offering a buying opportunity. You may be surer of a bullish resumption in the event of the price either respecting the band itself or failing to close below it when breaking below it.
You can tie in both Fibonacci entries with a consolidation entry. It’s best to await a closed candle to diminish a possible break, closing below the band. A close such as that signifies an impending bearish phase.
Conclusion
Trading indices with PrimeFin permits you to go long or short, leverage trade, and hedge existing positions. With such a broker, you can learn how to trade indices, decide if you would like to trade cash indices or futures indices, exercise practical risk management, and then simply monitor your positions. Correct forecasting is a lot easier with PrimeFin.